Reduce Cigarette Cravings with Acute Exercise

Catherine O’Brien
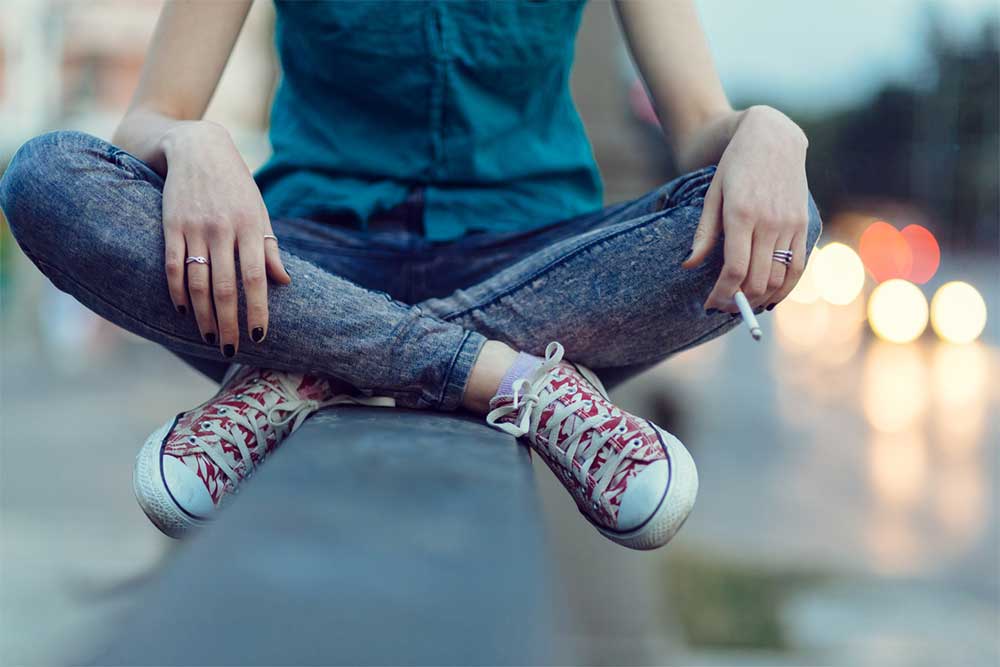
It is no secret that smoking is a major health hazard that significantly increases risk of cancer, heart disease, stroke and other health problems. That said, 20% of adult men and 16% of adult women smoke (American Heart Association, 2015). It is possible that, the sustaining prevalence of smokers is due, not to a lack of desire to quit but rather, to an inability to curb cigarette cravings. There are numerous pharmacological and therapeutic techniques used to promote smoking cessation and recent research suggests that acute exercise should also be added to the list of possible treatments.
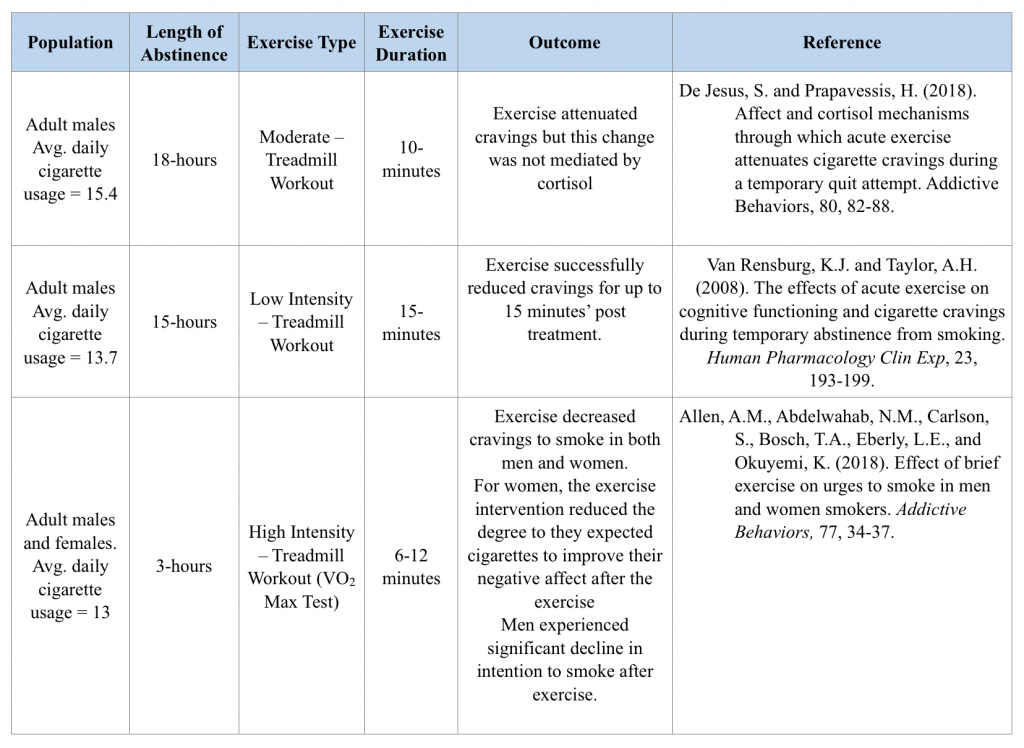
An acute bout of exercise can effectively attenuate cigarette cravings. In three separate studies, cravings were significantly decreased following an acute bout of exercise (Van Rensburg & Taylor, 2008; Allen, Abdelwahab, et al. 2018; De Jesus & Prapavessis, 2018). Participants in these studies were regular smokers who smoked, on average, more than 10 cigarettes per day. Prior to participation in the study, they were instructed to abstain from smoking for a determined number of hours (see details below). Participants then engaged in an acute bout of exercise for less than 20 minutes. The studies utilized exercise interventions with varying intensities ranging from low intensity to high intensity. In each of the three studies, participants reported significantly reduced cigarette cravings following the exercise intervention.
Related Article: Sitting Disease – The New Smoking
Research done by Van Rensburg et al. (2008) utilized a walking intervention and while smoking cravings reduced, they reported no change in cognitive functioning. They posit that, perhaps an increase in intensity of exercise would contribute to greater cognitive gains. Allen et al. (2018) found that both men and women experienced decreased cravings to smoke but that only women reported a reduction in the degree to which they expected the cigarettes to improve their negative affect after the exercise (Allen et al., 2018). Research done by DeJesus & Prapavessis (2018) showed that the acute bout of exercise was effective in reducing cravings but that this reduction was not coupled with a reduction in cortisol levels. They suggest that a more rigorous intervention may be needed in order to produce significant changes in cortisol.
The Takeaway:
- If you are trying to quit smoking and need help resisting cravings, exercise may be a good quitting partner
- While the results were promising for low, moderate, and high intensity, when doing short workouts, higher intensity is ideal. Try jumping rope or sprinting in intervals on the treadmill or cycle ergometer.
*Always consult your physician before beginning a new exercise routine.
Related Article: It’s Not Too Late To Become A Runner
You Might Like:
Can HIIT Improve Mental Health?
High intensity interval training (or HIIT for short) has fast become one of the most common forms of exercise on the planet. Used by athletes and regular gym goers alike, it has been applauded for...How to Incorporate HIIT in Every Workout
Over the last few years, high-intensity exercise modalities have become super popular. Think about the rise of CrossFit or even the creation of Orange Theory. Both of these workouts are incredibly popular, and both incredibly...The Effects of Sleep Quality and HIIT
Moji Kaviani Quality of sleep appears to be positively associated with both physical and psychological health (Halson, 2016; Lastella et al., 2012). Therefore, numerous studies examined the relationship between physical activity and sleep suggesting that...What is a High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) Workout Anyway?
Evan Stevens High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) is a huge ‘hit’ with exercise researchers and the general population alike. It is less time consuming and can imbue the same if not more benefits as traditional exercises...5 High-Intensity Interval Training Mistakes Athletes Make
Alyssa Bialowas High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is one of the hottest fitness trends right now, and because of this, many people have put their own spin on it to try and make it their own....5 Ways HIIT Improves Fitness in Women
Alyssa Bialowas Research poll after research poll, male and female adults express that one of the biggest barriers they face to frequent exercise is lack of time. One common assumption is that exercise and physical...References
Allen, A.M., Abdelwahab, N.M., Carlson, S., Bosch, T.A., Eberly, L.E., and Okuyemi, K. (2018). Effect of brief exercise on urges to smoke in men and women smokers. Addictive Behaviors, 77, 34-37.
De Jesus, S. and Prapavessis, H. (2018). Affect and cortisol mechanisms through which acute exercise attenuates cigarette cravings during a temporary quit attempt. Addictive Behaviors, 80, 82-88.
Van Rensburg, K.J. and Taylor, A.H. (2008). The effects of acute exercise on cognitive functioning and cigarette cravings during temporary abstinence from smoking. Human Pharmacology Clin Exp, 23, 193-199.
The American Heart Association (2015). Smoking: Do you really know the risks? Retrieved from http://www.heart.org/HEARTORG/HealthyLiving/QuitSmoking/QuittingSmoking/Smoking-Do-you-really-know-the-risks_UCM_322718_Article.jsp#.Ws5F7NMbMcg on April 10, 2018.
















